Self-healing roads are revolutionizing highway technology and reshaping the future of travel. These innovative roads are designed to repair themselves when cracks or damage occur, offering a solution to the costly and time-consuming process of road maintenance. By utilizing advanced materials like bacteria-infused concrete and capsule-infused asphalt, self-healing roads can minimize repairs and extend the life of roadways, making them safer and more durable.
 Pin
Pin Image from pexels
As climate change, heavy traffic, and extreme weather conditions put more strain on traditional roads, self-healing technology provides a sustainable alternative. The potential benefits of self-healing roads extend beyond reduced maintenance costs—they could improve driver safety, cut down on traffic disruptions, and reduce the environmental impact of construction projects. As self-healing roads become more widespread, they promise to transform how we travel, making our infrastructure smarter, greener, and longer-lasting.
Table of Contents
The Problem with Traditional Roads
 Pin
Pin Photo by Guillaume Meurice
Roads are lifelines for every country, connecting cities, villages, and people. Yet, they’re constantly under attack—weather, heavy vehicles, and time take a toll. Cracks appear, potholes form, and before you know it, repairs are overdue. Driving over damaged roads isn’t just uncomfortable; it’s unsafe and expensive. Governments spend billions yearly on maintenance, but the cycle never ends. You fix one part, and soon another needs attention. Imagine driving home, hitting a crack, and worrying if your tire will survive. It’s frustrating!
But here’s the thing: traditional roads don’t heal themselves. Once a crack forms, it’s game over unless humans intervene. That’s where the idea of self-healing roads comes in. Roads that can repair their own damage? It sounds futuristic, but it’s already happening. Scientists are working on materials that respond to cracks and heal naturally, reducing the need for constant repairs. This could change everything, saving money, time, and lives.
How Do Self-Healing Roads Work?
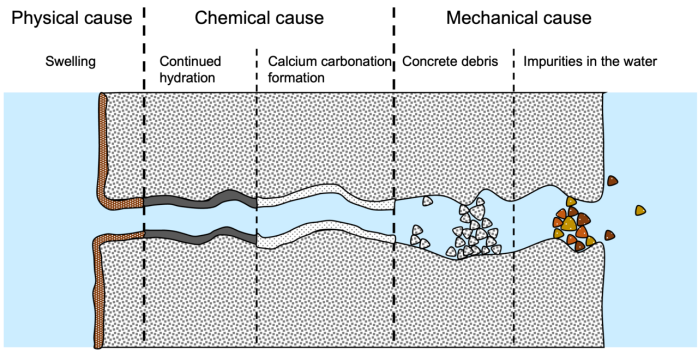 Pin
Pin Photo from Wikimedia Commons
Self-healing roads sound like science fiction, but they’re surprisingly simple. The concept revolves around advanced materials designed to repair themselves when damaged. One of the most promising innovations is asphalt mixed with tiny capsules of healing agents, like bitumen or polymer. When cracks appear, these capsules break open, filling the gaps and bonding the material back together. It’s like a wound healing on your skin!
Another fascinating approach uses bacteria-infused concrete. Yes, bacteria! These microorganisms activate when exposed to water or air, producing limestone to seal cracks. Imagine concrete that repairs itself every time it rains! Engineers are even exploring magnetic particles that, when heated, melt and fill gaps. This smart technology means roads could last decades longer than traditional ones.
The best part? These materials require minimal human intervention. Once laid, they do the job themselves. It’s not just a tech upgrade; it’s a revolution in how we think about infrastructure. But what’s driving this innovation? Let’s discuss next.
Why the World Needs Self-Healing Roads
 Pin
Pin Photo by Connor Forsyth
The need for self-healing roads isn’t just about convenience; it’s about survival. Every year, potholes and cracks cause accidents, injuries, and even fatalities. They also damage vehicles, leading to unexpected repair costs for drivers. For governments, the financial burden is staggering. Road maintenance and reconstruction projects eat up billions of dollars annually. Even with regular repairs, the results are temporary.
Climate change is making matters worse. Extreme weather—scorching summers, freezing winters, heavy rains—is brutal on roads. Expansion, contraction, and water damage are constant threats. Plus, with urban populations growing and vehicles increasing, roads are under more stress than ever.
Self-healing roads offer a solution to these challenges. They promise safer, longer-lasting infrastructure that reduces maintenance costs and environmental impact. Less repair work means fewer traffic disruptions and less carbon emissions from construction equipment. It’s a win-win. But while the idea is exciting, the road to implementation isn’t without hurdles.
Challenges in Making Self-Healing Roads a Reality
While self-healing roads are a groundbreaking idea, turning them into reality isn’t as easy as it sounds. One of the biggest obstacles is cost. The materials and technologies involved—like self-healing asphalt, bacteria-infused concrete, or magnetic particles—are more expensive than traditional options. Governments and contractors often hesitate to invest in untested methods, especially when budgets are tight.
There’s also the issue of scalability. It’s one thing to create self-healing materials in a lab, but deploying them on miles of highways is another story. Ensuring these materials work effectively under real-world conditions—extreme temperatures, heavy traffic, and varying climates—is a huge challenge.
On top of that, some of the technologies, like bacteria-based solutions, raise environmental concerns. What happens if those microorganisms escape into nearby ecosystems? And how do you ensure they remain active over decades?
The good news is that researchers and engineers are tackling these issues head-on. Progress is slow but steady.
Environmental Benefits of Self-Healing Roads
Self-healing roads aren’t just a technological breakthrough—they’re a win for the planet. Traditional road construction and maintenance are incredibly resource-intensive. Asphalt production, for example, relies heavily on fossil fuels, and the constant cycle of repairs creates tons of construction waste. Self-healing roads could significantly cut down on this environmental footprint.
By repairing themselves, these roads would drastically reduce the need for frequent maintenance. That means fewer roadwork projects, which translates to less equipment usage, lower emissions, and a smaller carbon footprint. Imagine driving through a city without the constant sight of construction zones—cleaner air, quieter streets, and smoother commutes.
Then there’s the issue of durability. Longer-lasting roads mean fewer materials needed over time, conserving resources like bitumen, gravel, and sand. Plus, with technologies like bacteria-based healing, we’re looking at eco-friendly innovations that could further minimize harm to the environment.
How Self-Healing Roads Will Impact Drivers and Daily Commutes
A world where road trips are smoother, commutes are faster, and you never have to swerve to avoid potholes. Self-healing roads promise exactly that. For drivers, it’s a game-changer. Damaged roads won’t stay damaged for long—they’ll repair themselves before issues worsen, ensuring a safer and more comfortable driving experience.
Fewer cracks and potholes mean fewer vehicle repairs. No more sudden tire blowouts or alignment issues caused by rough roads. This translates to real savings for drivers, not just in repair costs but in fuel efficiency. Smooth roads reduce wear and tear on cars and improve gas mileage.
Traffic disruptions due to roadwork could also become a thing of the past. With self-healing materials doing their job, maintenance crews won’t need to block lanes as often. For anyone who’s been stuck in endless construction-related traffic jams, this alone is a dream come true.
The Potential Impact on Developing Nations
Developing countries often struggle with infrastructure maintenance due to limited budgets and resources. Roads are vital for economic growth, connecting rural areas to cities, facilitating trade, and providing access to education and healthcare. Yet, poorly maintained roads remain a widespread issue, slowing progress and costing lives.
Self-healing roads could be a transformative solution. By reducing the need for constant repairs, these roads would lower long-term maintenance costs, making infrastructure investments more sustainable. Governments could redirect saved funds toward other critical areas like healthcare or education.
In rural regions, where access to skilled labor and machinery is limited, self-healing technology could make a huge difference. Roads that can repair themselves without constant human intervention ensure safer travel for people in remote areas.
These roads could withstand extreme weather conditions, a significant advantage for countries prone to floods, heat waves, or heavy rains. By investing in self-healing materials, developing nations could future-proof their infrastructure and boost their economies.
Integration with Smart City Technologies
 Pin
Pin Photo by Kostiantyn Stupak
Self-healing roads aren’t just a standalone innovation—they fit perfectly into the vision of smart cities. Roads that not only repair themselves but also communicate with vehicles and city infrastructure. These advanced roads could be embedded with sensors to monitor traffic flow, detect damage, and even report conditions in real time.
In a smart city, self-healing roads could work alongside other technologies like autonomous vehicles. Smooth, well-maintained roads are crucial for self-driving cars, ensuring they operate safely and efficiently. With integrated systems, your car could receive updates about road conditions ahead, optimizing your route and avoiding disruptions.
These roads could play a role in energy management. Some self-healing materials are compatible with energy-harvesting technologies, such as solar-powered surfaces or kinetic energy capture from moving vehicles. This dual-purpose approach aligns with the eco-friendly goals of smart cities.
By combining innovation and sustainability, self-healing roads could redefine urban living.
Industries Driving the Self-Healing Road Revolution
The push for self-healing roads isn’t coming from just one sector—it’s a collaboration between industries like construction, technology, and materials science. Leading companies in asphalt and concrete manufacturing are heavily investing in research to create cost-effective self-healing materials. Universities and research institutions are also playing a massive role, developing groundbreaking solutions like bacteria-based concrete and capsule-infused asphalt.
The tech industry is jumping on board too, integrating sensors and smart systems into road designs. These advancements ensure that self-healing materials work seamlessly in real-world conditions, from tracking wear and tear to optimizing repairs. Even the automotive industry has a stake in this transformation, as smoother, longer-lasting roads benefit vehicles and their performance.
Government support and funding are also crucial. Some countries are already testing pilot projects with self-healing materials, showcasing their potential to reduce infrastructure costs and improve safety. Together, these industries are laying the groundwork for a future where road repairs are no longer a burden.
The Long-Term Vision for Self-Healing Roads
The long-term vision for self-healing roads goes far beyond fixing cracks and potholes—it’s about reimagining the future of infrastructure. A world where roads last for decades with minimal maintenance, freeing up resources for other vital projects. With self-healing materials, highways, bridges, and urban streets could become more resilient, adapting to the challenges of climate change and increasing traffic demands.
In the future, we could see roads designed to generate energy, communicate with autonomous vehicles, and even absorb pollutants from the air. Self-healing technologies might extend beyond asphalt and concrete, influencing other areas like airport runways, parking lots, and cycling paths. This would create safer, more sustainable transportation networks for everyone.
The economic benefits are undeniable. Reduced maintenance costs, fewer traffic disruptions, and longer-lasting infrastructure mean significant savings for governments and taxpayers. For individuals, it’s about safer roads, smoother travel, and less stress.
Self-healing roads aren’t just a technological upgrade—they’re a bold step toward a smarter, greener, and more connected world.































