Pin
Pin Plants are the source of all life. They are the only things capable of catching the energy of the sun and turning it into living tissue. Without plants there would be no animals and no people.
There are millions of species of plants — from the giant oaks and redwoods, through beautiful orchids to humble grasses. But globally one group of plants is far more important than all the other types put together. These are the algae — singular alga — simple plants which usually live in water. Seventy per cent of the world’s surface is sea, and nearly all sea plants are algae.
 Pin
Pin 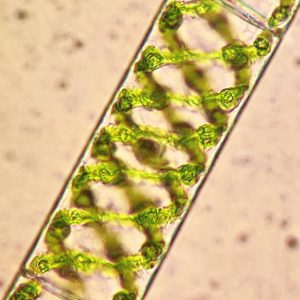 Pin
Pin Spirogyra
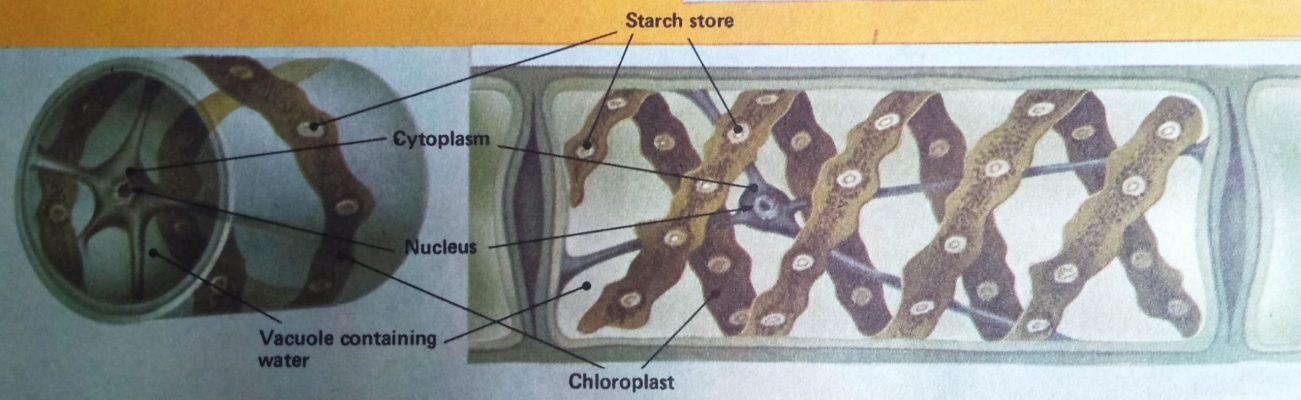
A long ‘necklace’ of green cells make up Spirogyra — an alga often found in ponds. The chloroplast spirals round the edge of each cell, and the cytoplasm stretches in thin strands from the cell edge to the central nucleus, but most of the plant is water.
 Pin
Pin Most people think of seaweeds when they think of algae, but the majority of algae are tiny single-celled plants which float in water. Chlamydomonas which grows in fresh water is a good example of this sort of alga. It is only one fiftieth of a millimetre long, but it is able to perform all the functions necessary to a living plant inside its one small cell.
 Pin
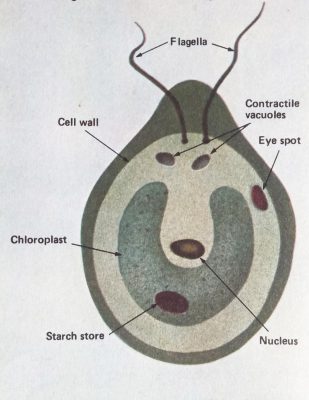
Pin Above: This simple plant is the fresh water alga Chlamydomonas. Our artist has added colours to show the plant’s structure clearly, but in fact it is colourless except for the green chloroplast that traps sunlight and turns it into living tissue.
Much of Chlamydomonas is made up of a structure called a chloroplast. This is green because it contains the pigment chlorophyll, which is able to absorb the energy of sunlight so that the plant can turn it into starch, which the plant then lives on. (This process is called photosynthesis.) It is chlorophyll which makes the leaves of all plants green.
As well as the chloroplast, Chlamydomonas contains a starch store, a nucleus containing genetic information, a red eye spot which is sensitive to light, and two whip-like flagella to move the plant about. (Many — although not all simple algae have the ability to move about.)
The rest of the plant is made up of the cytoplasm, in which the plant’s body functions are carried out, and contractile vacuoles which store and excrete water which enters from outside. Around the plant, holding it together, is the cell wall.
Although all algae contain chlorophyll, not all are green. This is because they contain other pigments that mask the green colour. In particular, there are brown algae, containing the pigment fucoxanthin, and red algae, containing phycobilins.
 Pin
Pin  Pin
Pin Above: Bladder wrack, a brown seashore seaweed. The bladders full of air keep the plant floating in the water.
There is a special reason why algae contain these other pigments while land plants do not. Water absorbs sunlight; so that even in clear tropical seas it is pitch black at depths greater than about 100 metres.
However, the different colours of light which make up sunlight are not all absorbed at the same rate. Red light is absorbed most, green and blue least. So at depth there is more green and blue light thar there is red.
 Pin
Pin Above: If you hold up a glass of water, you have no difficulty in looking straight through it. Nevertheless, water does absorb light, although it does not do so at the same rate for all the different colours that make up white light. It absorbs red light first, blue last. This means that different types of algae live at different depths. Green algae can only live on red light, so they are only found in shallow water. Red algae can live on blue light and are therefore able to grow at greater depth. Brown algae can use greenish light and can live in water of medium depth.
Chlorophyll absorbs red light — which is why it looks green, because the green light is reflected — phycobilins absorb green and blue light, which is why they look red. So red algae, containing phycobilins, can live at greater depths where there is only green and blue light. Green algae must live in shallow water where there is red light.
Brown algae usually live at medium depths between the green and red algae. Many, however, are seaweeds that live on the seashore.
Seaweeds are algae which have developed into a many-celled form. Some grow as large as the biggest land plants — up to 60 metres long but most are about one metre. The major differences between them and land plants is that they have no real roots, stems or leaves.
 Pin
Pin Seaweeds have got to be tough to survive on the seashore. Clinging to the rocks, they are constantly bombarded by the waves and dried and rewetted as the tides rise and fall. To survive these conditions, they have developed thick rubbery ‘skins’.
 Pin
Pin  Pin
Pin  Pin
Pin Algae are not only the food source for all the fish in the oceans, brown seaweeds are also collected throughout the world to make alginates — chemicals used to make cosmetics, polishes, paints, car tyres and even ice cream!
But, perhaps most importantly, algae are responsible for producing the very air we breathe. Oxygen Is given off as a by-product during photosynthesis, and by far the largest source of oxygen in the world is the billions of minute algae in the sea.
Angiosperms
The most important group of plants can be argued to be angiosperms, also known as flowering plants.
Angiosperms are a diverse group of plants that have the unique ability to produce flowers, fruits, and seeds. They make up the majority of plant species on Earth and play a crucial role in sustaining life.
 Pin
Pin One of the key characteristics that make angiosperms so significant is their ability to produce flowers. Flowers are reproductive structures that contain several parts, including petals, sepals, stamens, and pistils. These structures attract pollinators such as insects, birds, or bats, which aid in the transfer of pollen between flowers, leading to fertilization. This process ensures genetic diversity and allows for the production of seeds, which are essential for the continuation of plant species.
Furthermore, angiosperms are unique in their ability to produce fruits. Fruits develop from the fertilized ovary of a flower and serve as protective structures for seeds. They come in various forms, such as berries, nuts, or capsules, and offer a wide range of benefits. Fruits are not only a valuable source of nutrition for animals, including humans, but they also play a crucial role in seed dispersal. Animals consume the fruits and subsequently disperse the seeds through their digestive system or by carrying them to different locations, aiding in the spread and colonization of plant species.
Angiosperms have also evolved a variety of adaptations that have allowed them to colonize diverse habitats around the world. They can be found in every terrestrial ecosystem, from lush rainforests to arid deserts and icy tundras. This adaptability is largely due to their ability to modify their leaves, stems, and roots to withstand different environmental conditions. For example, desert plants have developed thick, waxy leaves to reduce water loss during hot and dry conditions, while aquatic plants have adapted to absorb nutrients from water through their specialized root structures.
Moreover, angiosperms provide numerous ecosystem services that are essential for maintaining the health and balance of ecosystems. They contribute to soil formation and prevent erosion by anchoring soil with their roots. The process of photosynthesis, in which plants convert carbon dioxide into oxygen, is carried out by angiosperms and plays a vital role in regulating Earth’s atmosphere. Plants also act as natural air filters, absorbing pollutants and releasing clean oxygen into the atmosphere. Additionally, they provide habitat and food for a wide range of organisms, supporting biodiversity and promoting ecological stability.
From an economic standpoint, angiosperms are incredibly vital. They are the primary source of food for humans and animals, providing essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals. Many staple crops, including grains, fruits, vegetables, and nuts, are angiosperms. Moreover, angiosperms contribute to various industries such as agriculture, forestry, horticulture, and pharmaceuticals. They provide raw materials for the production of clothing, paper, wood products, and medicines, among others.
In conclusion, angiosperms, or flowering plants, are undoubtedly the most important group of plants. Their ability to produce flowers, fruits, and seeds, along with their adaptability, ecosystem services, and economic significance, make them the foundation of terrestrial life. Without angiosperms, the balance and functioning of ecosystems would be severely impacted, and numerous industries and food sources would be compromised.
 Pin
Pin  Pin
Pin The most important group of plants in maintaining carbon dioxide levels, oxygen production, and mitigating climate change are the trees and forests. Their key roles include:
Trees and forests are critical in maintaining carbon dioxide levels, oxygen production, and mitigating climate change through their roles in carbon sequestration, oxygen production, cooling, water cycle regulation, biodiversity support, soil preservation, and acting as natural carbon sinks. Protecting and restoring forests is crucial for addressing climate change and sustaining the health of our planet.
The most important group of plants, or the primary producers, contribute significantly to the overall health and balance of the environment in several ways:
Overall, the primary producers, or most important group of plants, have a profound impact on the health and balance of the environment by sustaining life through oxygen production, carbon dioxide absorption, soil stabilization, water cycle regulation, habitat creation, and nutrient cycling.
FAQs about the Most Important Group of Plants:
The most important group of plants refers to angiosperms or flowering plants. These plants are highly diverse and make up the majority of plant species on Earth. They play a crucial role in various ecosystems and are vital for the sustenance of life on our planet.
Flowering plants are considered the most important group for several reasons. Firstly, they are the primary producers in most ecosystems, converting sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into organic compounds through photosynthesis. This process forms the basis of the food chain, providing sustenance for herbivores and subsequently carnivores.
Flowering plants reproduce through the process of pollination. They produce flowers that have reproductive organs, including male stamens (with pollen) and female pistils (with ovules). Pollination occurs when pollen is transferred from the stamens to the pistils, either by wind, insects, birds, or other animals. After successful pollination, the ovules are fertilized, leading to the development of seeds within the fruit.
Flowering plants have immense economic importance. They serve as a primary source of food for humans and animals. Many staple crops, such as wheat, rice, corn, and fruits, are flowering plants. Additionally, flowering plants are the source of many important plant-based products, including timber, medicinal plants, textiles (cotton), oils (olive, sunflower), and spices (pepper, cinnamon).
Flowering plants are crucial for maintaining ecosystem stability. They help prevent soil erosion by holding the soil together with their roots. Their canopies also shade the ground, reducing evaporation and maintaining moisture levels in the soil. Additionally, flowering plants provide habitat and food for various animal species, promoting biodiversity and ecological balance.
No, flowering plants exhibit immense diversity in terms of their size, shape, habitat, and reproductive strategies. They can be found in diverse environments ranging from deserts to rainforests. Some flowering plants are annuals, completing their life cycle within one year, while others are perennials, living for several years. The enormous variety of flowers, leaves, and fruit structures among flowering plants is a testament to their evolutionary success.
Yes, flowering plants have shown remarkable adaptability to changing environmental conditions through mechanisms such as genetic diversity, physiological changes, and symbiotic interactions with pollinators and other organisms. This adaptability allows them to survive and thrive in various habitats, from the freezing Arctic tundra to scorching deserts.
Conservation efforts for flowering plants primarily involve protecting their natural habitats and preserving endangered species. Efforts include establishing protected areas, seed banks, and botanical gardens for ex-situ conservation. Conservationists also work towards raising awareness about the importance of flowering plants and promoting sustainable practices to prevent habitat destruction and loss of biodiversity.
Individuals can contribute to the preservation of flowering plants by planting native species in their gardens, conserving water, avoiding the use of harmful pesticides, and supporting sustainable agriculture and horticulture practices. Educating oneself and others about the importance of flowering plants and their conservation is also crucial in promoting collective action.
Yes, flowering plants face various threats, including habitat destruction due to urbanization and deforestation, climate change, invasive species, pollution, over-harvesting, and diseases. These threats can lead to the extinction of plant species, disrupting ecosystems and impacting the overall health of our planet. Hence, it is essential to work towards their conservation and sustainable use.