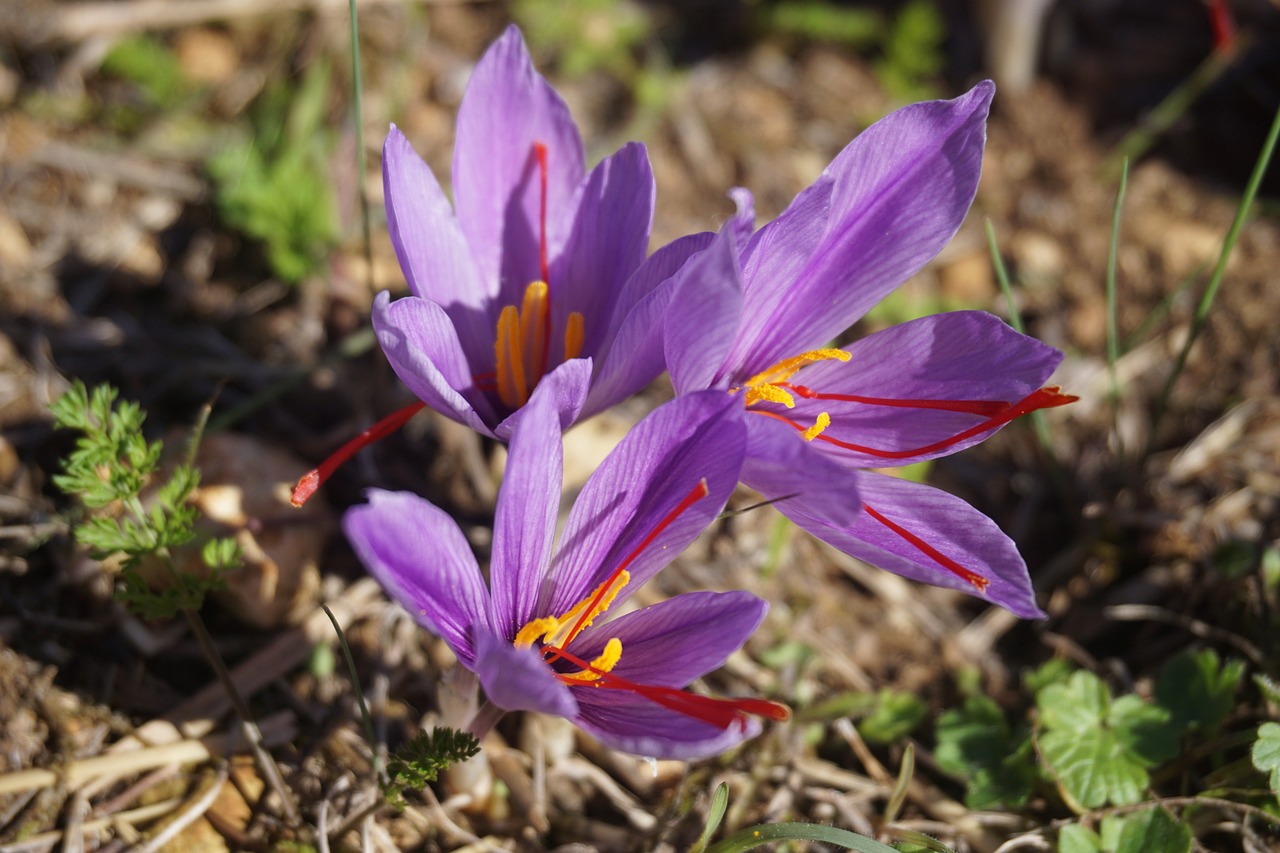
Saffron, often referred to as the “red gold,” is one of the world’s most expensive spices, prized for its distinct flavor and vibrant color. Traditionally, saffron is cultivated in soil-based agriculture. However, in recent years, hydroponic and aeroponic methods have gained popularity due to their numerous advantages. This guide will delve into the specifics of aeroponic saffron farming, providing insights for beginners.
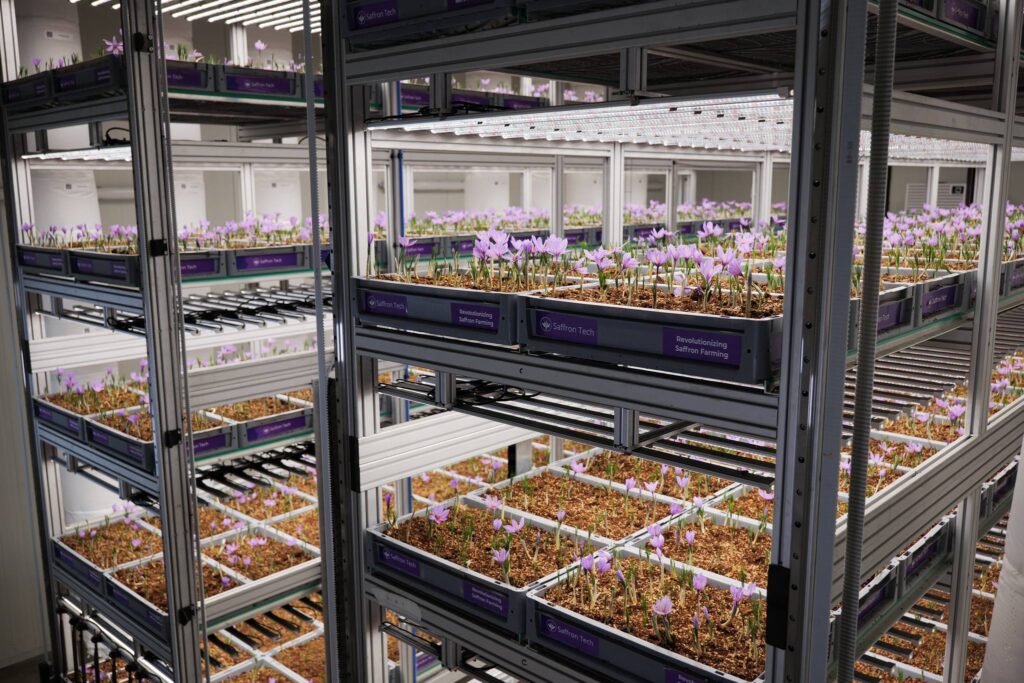 Pin
Pin Image by israelagri2
Table of Contents
Understanding Aeroponics
Aeroponics is a type of hydroponic cultivation where plants are grown with their roots suspended in the air. Nutrient-rich mist is sprayed onto the roots at regular intervals, providing the essential elements for growth. This method eliminates the need for soil altogether, offering several benefits such as increased yields, reduced water consumption, and the ability to grow plants in controlled environments.
Setting Up an Aeroponic Saffron Farm: Essential Requirements
Aeroponic saffron farming offers a promising alternative to traditional soil-based cultivation. This method involves growing saffron plants with their roots suspended in the air and misted with a nutrient-rich solution. To establish a successful aeroponic saffron farm, it is essential to have the following setup requirements:
1. Aeroponic System
- Type: Choose an aeroponic system that suits your space and experience level. Popular options include vertical aeroponic towers, horizontal aeroponic systems, and mist systems.
- Size: Consider the size of your saffron farm and the number of plants you intend to grow. Select a system that can accommodate your needs.
- Quality: Invest in a high-quality aeroponic system to ensure optimal plant growth and longevity.
2. Nutrient Solution
- Formula: Use a commercially available hydroponic nutrient formula specifically designed for saffron. Alternatively, you can create your own nutrient solution by carefully following recommended ratios of macronutrients and micronutrients.
- pH: Maintain the pH of the nutrient solution within the optimal range for saffron growth. Use a pH meter to monitor and adjust the pH as needed.
3. Water Source
- Quality: Ensure a reliable source of clean, high-quality water for your aeroponic system. Avoid using hard water or water containing impurities that can harm the plants.
- Filtration: Consider using a water filtration system to remove any contaminants or impurities that may be present in your water source.
4. Lighting
- Intensity: Saffron plants require sufficient light for photosynthesis. Use artificial lighting, such as LED grow lights, to provide the necessary light intensity.
- Duration: Ensure the plants receive adequate light for the appropriate duration. Saffron plants typically require 12-16 hours of light per day.
5. Temperature and Humidity Control
- Temperature: Maintain a suitable temperature range for saffron growth. The ideal temperature for saffron plants is typically between 65-75°F (18-24°C).
- Humidity: Monitor and control the humidity levels in your aeroponic system. Saffron plants prefer moderate humidity levels, but excessive humidity can lead to disease and mold.
6. Air Circulation
- Ventilation: Ensure proper air circulation within your aeroponic system to prevent the buildup of moisture and carbon dioxide. Adequate ventilation can help maintain a healthy growing environment.
7. Monitoring Equipment
- pH Meter: Use a pH meter to monitor the pH of the nutrient solution and make adjustments as needed.
- Temperature and Humidity Sensors: Install temperature and humidity sensors to track environmental conditions within your aeroponic system.
- Nutrient Level Tester: Consider using a nutrient level tester to monitor the levels of essential nutrients in the nutrient solution.
By carefully considering and addressing these setup requirements, you can create a successful aeroponic saffron farm that produces high-quality saffron.
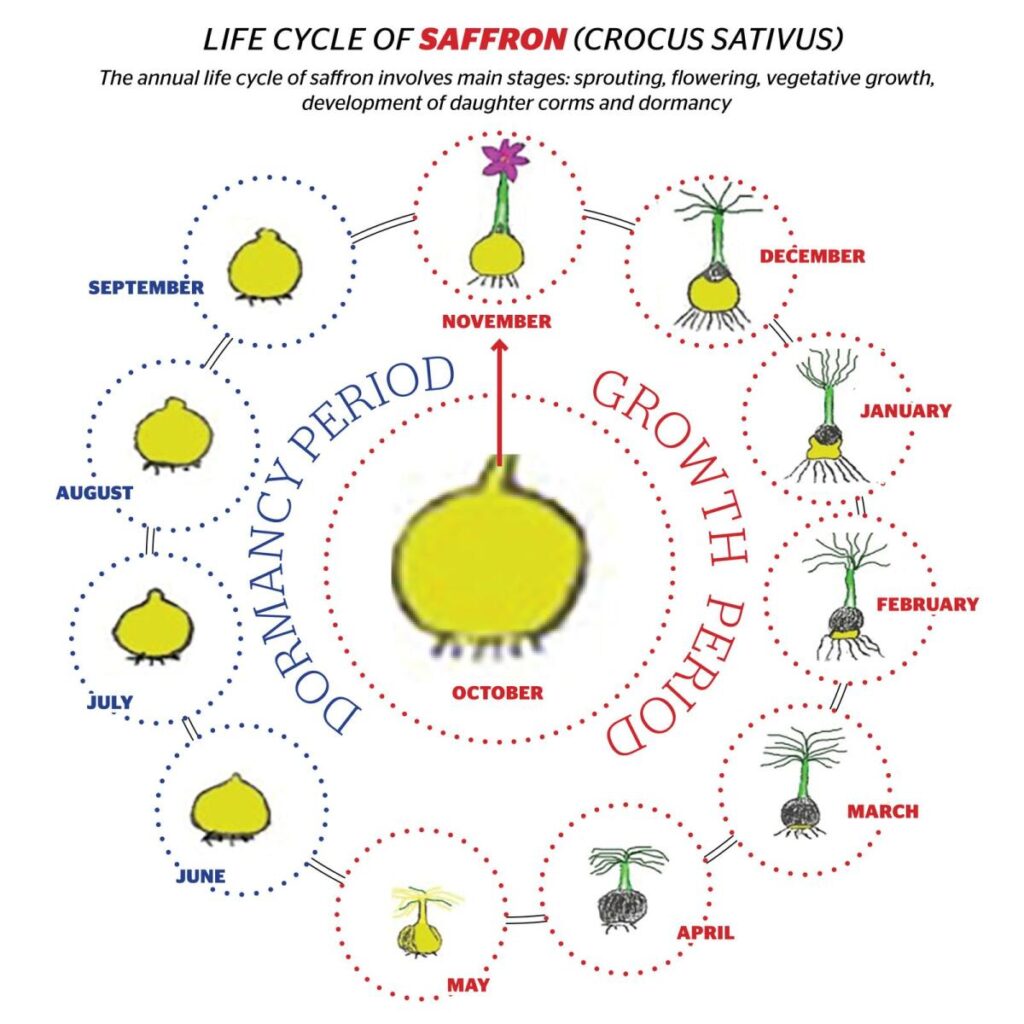
The Growth Cycle of Saffron in Aeroponics
 Pin
Pin Image from khaleejtimes
Saffron, a prized spice known for its vibrant color and distinct flavor, is traditionally grown in soil-based agriculture. However, aeroponic cultivation, a method that involves growing plants with their roots suspended in the air and misted with a nutrient-rich solution, offers several advantages for saffron production. This article will delve into the growth cycle of saffron in aeroponics.
1. Bulb Preparation and Planting
- Bulb Selection: High-quality saffron bulbs are essential for successful aeroponic cultivation. Choose bulbs that are firm, plump, and free from diseases.
- Planting: Place the bulbs in the aeroponic system, ensuring they are securely supported. The bulbs should be planted at an appropriate depth to promote healthy root development.
2. Root Development
- Nutrient Misting: The aeroponic system will deliver a nutrient-rich mist to the roots at regular intervals. This mist provides the essential elements necessary for root growth and development.
- Root Health: Aeroponics promotes the development of healthy and vigorous root systems. This is because the roots are constantly exposed to oxygen and nutrients, which can enhance their growth and function.
3. Shoot Growth and Flowering
- Light Exposure: Saffron plants require sufficient light for photosynthesis. Ensure the aeroponic system is placed in an area with adequate lighting or use artificial grow lights.
- Flowering: After several weeks of growth, saffron plants will begin to produce flowers. The flowers are typically a vibrant purple or yellow color.
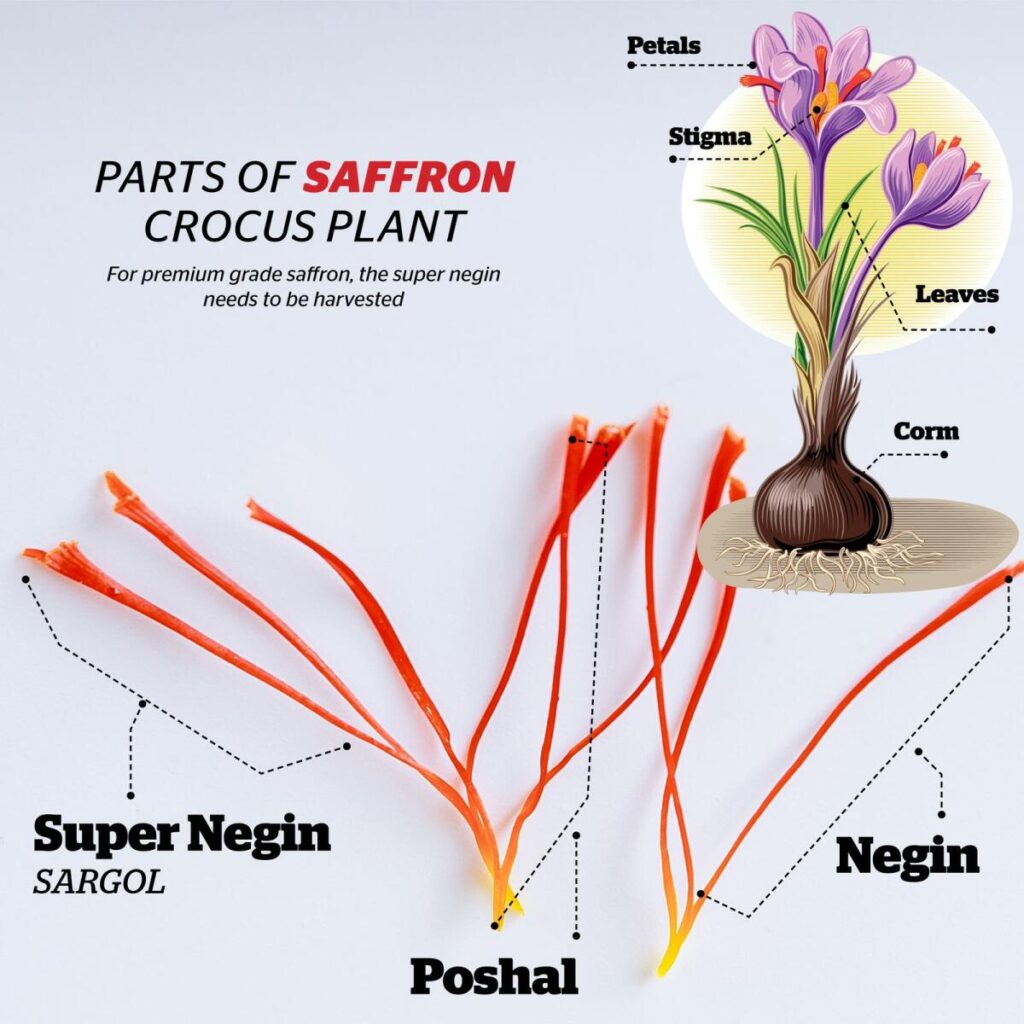
4. Stigma Harvesting
- Stigma Identification: The saffron stigma, the part of the flower that is harvested for its spice, is located within the center of the flower. It is typically a deep red or orange color.
- Harvesting: Carefully remove the stigmas from the flowers. This can be done by hand or with the aid of tweezers.
5. Bulb Regeneration
- Bulb Growth: After harvesting the stigmas, the saffron bulbs will continue to grow and develop. This process is essential for ensuring a continuous supply of saffron.
- Bulb Division: In some cases, the bulbs may become overcrowded. If this occurs, they can be divided and replanted to promote healthy growth and higher yields.
 Pin
Pin Image from khaleejtimes
Advantages of Aeroponic Saffron Cultivation
- Higher Yields: Aeroponics can produce higher yields of saffron per square foot compared to traditional soil-based methods.
- Improved Quality: Saffron grown in aeroponic systems often has a higher quality and flavor profile.
- Reduced Water Consumption: Aeroponics involves the efficient use of water, as the nutrient mist is recycled and reused.
- Pest and Disease Control: The controlled environment of aeroponic systems can help prevent pest and disease infestations.
Aeroponic saffron cultivation offers a promising alternative to traditional methods. By providing a controlled environment and optimizing nutrient delivery, aeroponics can enhance saffron production and ensure a consistent supply of this valuable spice.
Preparing Saffron Corms for Aeroponic Cultivation
Selecting Quality Saffron Corms
The foundation of successful saffron cultivation lies in the quality of the corms. Here are key factors to consider when selecting saffron corms for aeroponic cultivation:
- Size and Weight: Opt for plump, firm, and evenly sized corms. Heavier corms often indicate better quality and higher yield potential.
- Color: Saffron corms should have a light brown or tan color. Darker or discolored corms may be damaged or diseased.
- No Damage or Pests: Ensure the corms are free from any signs of physical damage, rot, or pests.
- Source and Reputation: Purchase corms from reputable suppliers or growers with a proven track record of providing high-quality saffron.
Disinfection Process
To minimize the risk of introducing diseases or pests into the aeroponic system, it’s essential to disinfect the saffron corms before planting. Here’s a recommended disinfection procedure:
- Soak in Potassium Permanganate Solution: Prepare a dilute solution of potassium permanganate (1-2 grams per liter of water). Soak the corms in this solution for 30-60 minutes. Potassium permanganate is a powerful disinfectant that can kill harmful microorganisms.
- Rinse Thoroughly: After soaking, rinse the corms thoroughly with clean water to remove any residual potassium permanganate.
Pre-germination Care
Before planting the saffron corms in the aeroponic system, it’s beneficial to undergo a pre-germination process to promote faster and more uniform germination. Here are some effective methods:
I. Moist Paper Towel Method:
- Place a damp paper towel in a sealed plastic bag.
- Place the saffron corms on the wet paper towel, ensuring they are not touching each other.
- Seal the bag and store it in a warm, dark place.
- Check the paper towel regularly to ensure it remains moist. The corms should start to sprout within a few weeks.
II. Sand or Perlite Method:
- Fill a container with a sterile growing medium like sand or perlite.
- Moisten the medium slightly.
- Place the saffron corms on the medium, ensuring they are not touching each other.
- Cover the container with a lid or plastic wrap.
- Store the container in a warm, dark place.
- Check the moisture level regularly and mist the medium lightly as needed.
Once the corms have developed healthy roots, they are ready to be planted in the aeroponic system.
Getting Started with Aeroponic Saffron Farming
- Choose an Aeroponic System: There are various aeroponic systems available, including vertical aeroponic towers, horizontal aeroponic systems, and mist systems. Select a system that suits your space and experience level.
- Prepare the Nutrient Solution: Saffron requires a specific nutrient solution tailored to its needs. Use a commercially available hydroponic nutrient formula or create your own by following recommended ratios.
- Obtain Saffron Bulbs: Procure high-quality saffron bulbs from a reputable supplier. Ensure they are healthy and free from diseases.
- Planting the Bulbs: Place the saffron bulbs in the aeroponic system according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Ensure the bulbs are securely supported to prevent them from falling.
- Provide Adequate Lighting: Saffron requires sufficient light for photosynthesis. Use artificial lighting, such as LED grow lights, to provide the necessary light intensity and duration.
- Misting Schedule: Establish a regular misting schedule to ensure the roots receive adequate moisture and nutrients. Adjust the misting frequency and duration based on the system’s requirements and environmental factors.
- Monitor and Adjust: Regularly monitor the nutrient solution pH, temperature, and oxygen levels. Make adjustments as needed to maintain optimal growing conditions.
- Harvest and Store: Saffron is typically harvested in the fall. Carefully remove the stigmas from the saffron flowers and store them in an airtight container in a cool, dark place.
Ensuring Success: Maintenance and Monitoring of Aeroponic Saffron Farming
Aeroponic saffron farming offers a promising alternative to traditional soil-based cultivation. However, to ensure optimal growth and yield, it is essential to implement proper maintenance and monitoring practices. This article will delve into the key aspects of maintaining and monitoring your aeroponic saffron farm.
1. Regular Nutrient Solution Monitoring
- pH Levels: Monitor the pH of the nutrient solution regularly. Saffron plants thrive in a slightly acidic environment with a pH between 5.5-6.5. Use a pH meter to measure the pH and adjust it as needed using pH up or pH down solutions.
- Nutrient Levels: Periodically test the nutrient levels in the solution to ensure the plants are receiving adequate amounts of essential nutrients. Use a nutrient level tester or consult a hydroponics expert for guidance.
- Nutrient Replenishment: Replenish the nutrient solution as needed to maintain optimal levels. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for nutrient dosing.
2. Temperature and Humidity Control
- Temperature Monitoring: Use temperature sensors to monitor the temperature within your aeroponic system. Saffron plants prefer a temperature range of 65-75°F (18-24°C). Make adjustments to your heating or cooling system as necessary.
- Humidity Control: Monitor humidity levels to ensure they are within the optimal range for saffron growth. Excessive humidity can lead to mold and disease. Use dehumidifiers or fans to regulate humidity if needed.
3. Root Health Inspection
- Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect the roots of your saffron plants for signs of health issues. Look for root rot, discoloration, or stunted growth.
- Root Pruning: If you notice any unhealthy roots, carefully prune them away to prevent the spread of disease.
4. Pest and Disease Control
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections of your saffron plants for signs of pests or diseases. Look for aphids, spider mites, or fungal infections.
- Preventive Measures: Implement preventive measures such as biological controls, natural predators, or neem oil to deter pests and diseases.
5. Lighting Maintenance
- Bulb Replacement: Regularly inspect and replace any burnt-out or dimming grow lights. Ensure that the lights are providing adequate light intensity for optimal saffron growth.
- Light Cleaning: Clean the surfaces of your grow lights to remove dust and other debris that can reduce light output.
6. System Maintenance
- Cleaning: Regularly clean your aeroponic system to prevent the buildup of algae, mineral deposits, or other contaminants. Follow the manufacturer’s cleaning instructions.
- Equipment Maintenance: Ensure that all equipment, such as pumps, misters, and timers, are functioning properly. Replace any faulty components as needed.
By diligently following these maintenance and monitoring practices, you can optimize the growth and productivity of your aeroponic saffron farm, ensuring a bountiful harvest of this valuable spice.
Harvesting and Processing Saffron in Aeroponic Farming
Harvesting
- Timing: Saffron harvesting typically occurs in the early morning, as the flowers are most likely to be fully open and the stigmas (the valuable part of the flower) are fresh and moist.
- Manual Process: The harvesting of saffron in aeroponic systems is still largely a manual process. Workers carefully pluck the stigmas from the flowers, often using tweezers or small scissors to ensure precision.
- Gentle Handling: Due to the delicate nature of the stigmas, it’s essential to handle them with care to prevent damage. Rough handling can result in the loss of color and aroma.
Processing
- Sorting and Cleaning: The harvested stigmas are sorted to remove any impurities, such as leaves or flower petals. They are then cleaned to ensure they are free of dirt or debris.
- Drying: Drying is a critical step in preserving the quality and aroma of saffron. The stigmas are typically dried in a warm, dry environment, either in the shade or using a dehydrator. Drying reduces moisture content, preventing spoilage.
- Grading: Dried saffron is often graded based on its quality, color, and aroma. Higher-quality saffron typically has a deeper red color and a more intense aroma.
- Packaging: Once dried and graded, the saffron is packaged for storage or sale. It is usually packaged in small quantities, as it is a highly concentrated spice.
Key Considerations for Aeroponic Saffron Harvesting and Processing:
- Hygiene: Maintaining a clean and sanitary environment is crucial to prevent contamination of the saffron.
- Efficiency: Developing efficient harvesting and processing methods can help maximize yields and minimize costs.
- Quality Control: Implementing quality control measures can ensure that the final product meets high standards of purity and potency.
FAQs: Growing Saffron Without Soil: A Beginner's Guide to Aeroponic Saffron Farming
Aeroponic saffron farming is a method of growing saffron plants without soil. The plants’ roots are suspended in the air and misted with a nutrient-rich solution. This technique offers several advantages, including higher yields, reduced water consumption, and a controlled environment.
Aeroponic saffron farming provides several benefits over traditional soil-based methods, such as:
- Increased yields
- Reduced water consumption
- Controlled environment
- Pest and disease control
- Year-round production
Yes, you can grow saffron indoors using aeroponics. You’ll need to provide adequate lighting, temperature control, and humidity control.
You’ll need an aeroponic system, nutrient solution, saffron bulbs, lighting, temperature and humidity control, and monitoring equipment.
The frequency of changing the nutrient solution depends on several factors, including the size of your system, the number of plants, and the nutrient levels. As a general guideline, aim to change the solution every 1-2 weeks.
The ideal temperature for saffron growth is between 65-75°F (18-24°C). The humidity should be moderate, but avoid excessive humidity to prevent mold and disease.
Saffron plants typically take 6-8 weeks when taken proper care, to flower from planting.
Saffron stigmas are harvested by hand or with tweezers. Carefully remove the stigmas from the flowers.
Yes, you can save saffron bulbs for future plantings. After harvesting the stigmas, the bulbs will continue to grow and develop.
If your saffron plants are not growing well, check the nutrient levels, pH, temperature, and humidity. Ensure that the plants are receiving adequate light and that there are no pests or diseases affecting them.
Regular monitoring, preventive measures, and good hygiene practices can help prevent pests and diseases. Consider using biological controls, natural predators, or neem oil.






























