 Pin
Pin Oil, gas and coal, which are the world’s supply of fossil fuels, will sooner or later, run out. In preparation for this, considerable work is already being done to find alternative forms of energy.
Nuclear power is just one of the considerations. Another natural and perhaps most obvious source of energy, is the sun. Here, we give thought to the many other alternative energy sources.
Variations
Of course, many of the other sources are really variations of solar energy. They rely on rain, caused by the Sun evaporating the seas, on wind powered by the Sun’s heat, and on waves powered by the winds. Even methane gas generators are solar collectors of a sort — they recycle the energy in waste which originally came from green plants photo-synthesising in sunlight. Only geothermal power (power from the heat of the Earth’s core) and tidal power do not tap the Sun’s near-boundless energy.
All the alternative sources, however, do have one thing in common. They do not rely on fossil fuels and therefore there is no reason why they should not supply power for as long as Man can imagine.
Some of the projects described here are for large-scale schemes which would generate electricity suitable for adding to the national grid of power cables. But some energy is always lost when it is converted from one form to another and the real future for alternative energy sources is more probably many small, local ‘power Stations’ rather than a few huge energy factories.
For centuries — before the invention of the steam engine — water-wheels and windmills supplied the power for grinding grain and for other simple tasks such as pumping water. It would be unrealistic to think that old-fashioned Don Quixote style sail windmills will again be built; nowadays they would be very expensive to construct indeed. Moreover a great number would be required to produce the amount of power used in modern society, many thousands of times more than that used in medieval times.
Nevertheless a 20-metre windmill can give quite useful amounts of power — say 75 kW — enough to supply a small village, although hardly enough to send halfway across the country on pylons.
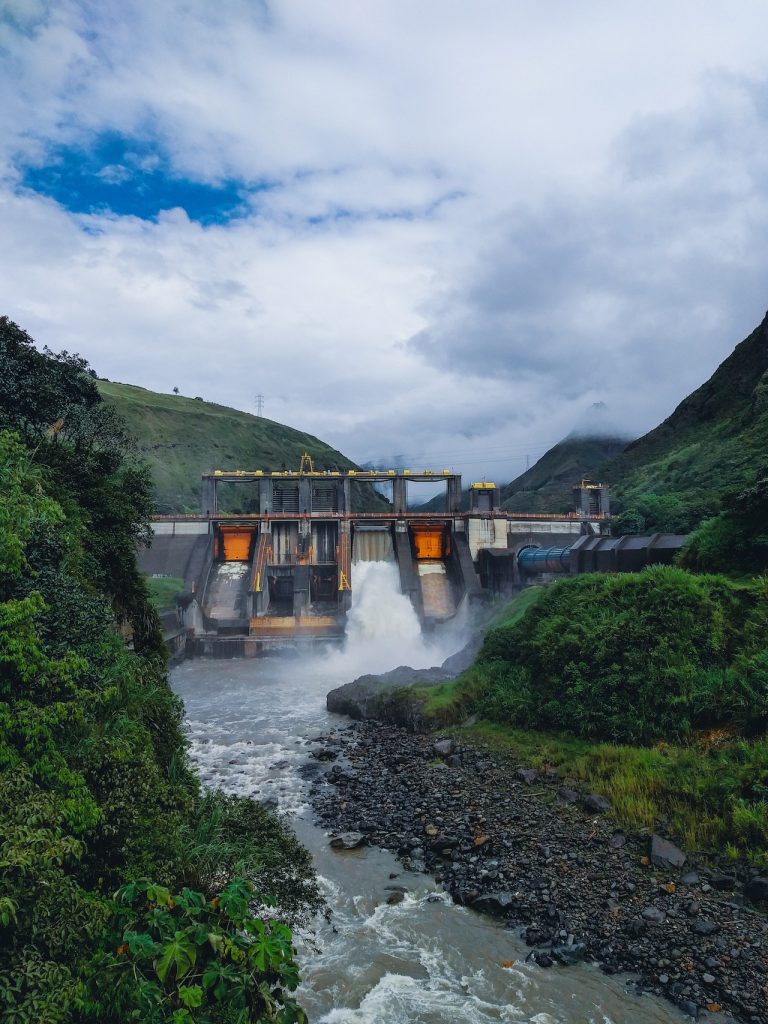
The modern equivalent of the water-wheel — the turbine — is used extensively already to make power. Hydro-electric power stations are common wherever there is mountainous terrain and plentiful water.
Biogas
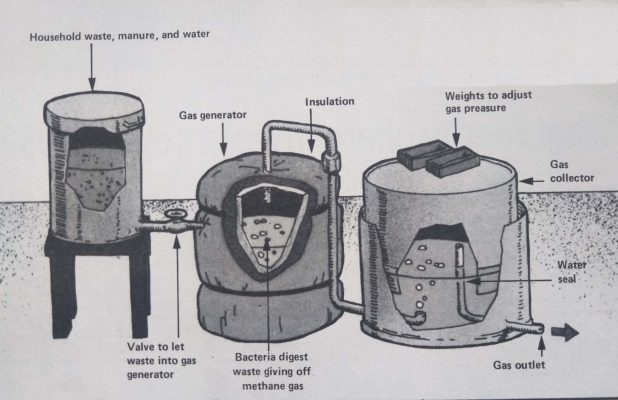
In agricultural areas, particularly in rural countries like India, human and animal manure, along with vegetable waste, can also provide useful energy on a local scale. In biogas plants, bacteria are used to rot down the manure giving off the gas methane, which can be burnt to heat cookers, machinery or even cars.
But in a future new world, reliant upon alternative energy sources, cars would almost certainly be a thing of the past. They use far too much energy. Trains are more economical and are the-best fast alternative. At sea, sailing ships are very cheap to run energy-wise! But perhaps the best alternative energy source as far as inland transport is concerned is leg power. You really can’t better the bike!
HYDRO-ELECTRIC POWER
Rivers and streams have been used to drive mills since the earliest times. More recently, the power of flowing water has been used to drive electricity generators. Unfortunately, not all rivers are suitable to drive present-day generators. However, as it is certain that water power will continue to be an important source of energy for the future, a great deal of work is being put into finding ways of making the generating systems more efficient — able to use more slowly flowing water for example.
 Pin
Pin 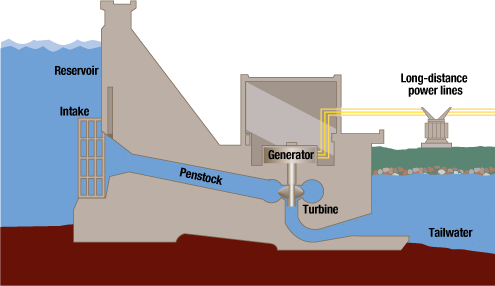 Pin
Pin BIOGAS GENERATOR
Biogas plants like this are already in operation in many places. The gas is produced by bacteria as they break down manure and waste.
 Pin
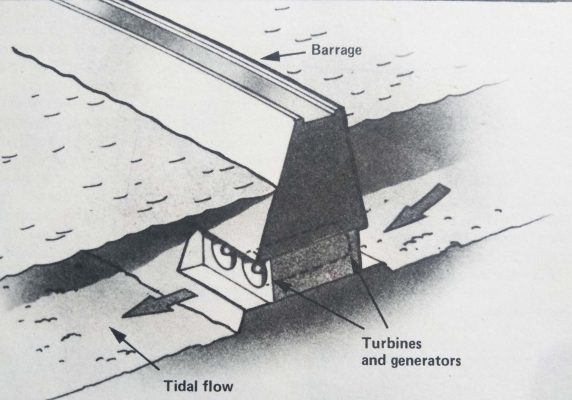
Pin TIDAL BARRAGES
A great deal of energy is available in the rise and fall of the tides. If a barrage, or dam, is built across a bay, it traps water behind it. As the tide runs out, this water is allowed to run out rough turbines, which generate electricity as they spin. In some tidal barrages, the turbines can work in either direction, so generating electricity both as the tide rises and as it falls. A tidal barrage has been in operation on for many years in France.
 Pin
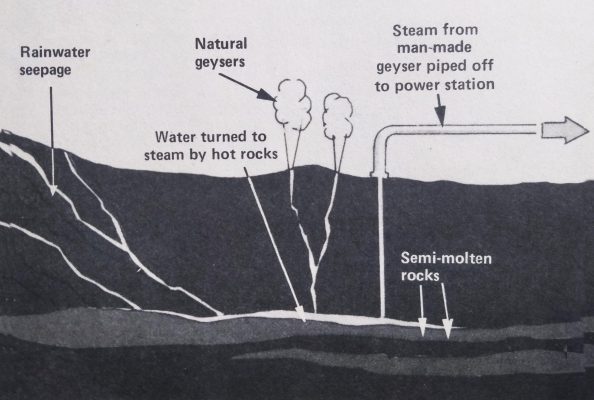
Pin GEOTHERMAL POWER
The centre of the Earth is hot enough to melt rock. This molten rock occasionally escapes as the lava spewed from volcanoes. When water seeps down into these hot rocks, it boils — escaping as geysers. In many countries, this naturally hot water is used to power electricity generators, and much work is going on to make more use of this power source, even in countries with no natural geysers. If a pipe is drilled down to hot rocks, it can make a man-made geyser just as useful as the natural thing.
 Pin
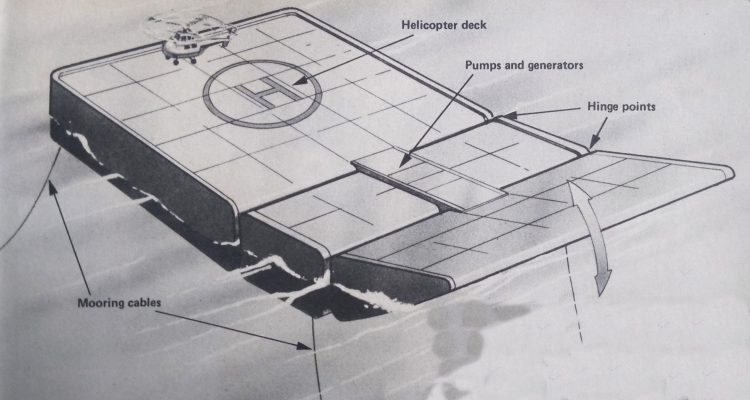
Pin WAVE POWER
There are many ways of using the energy in waves. Our below diagram shows the rafts designed by Sir Christopher Cockerell, inventor of the Hovercraft. The waves raise and tower hinged bow sections and this works hydraulic pumps which drive electricity generators.
 Pin
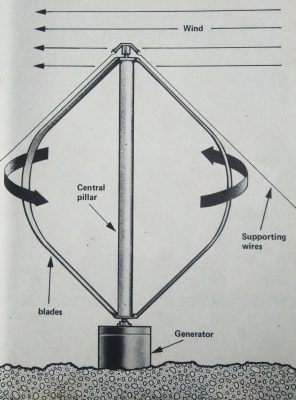
Pin WINDMILLS
There are many modern windmill designs. This one does not need to be turned to face into the wind, and, even in a gale, cannot go too fast because over-speeding makes the blades bend, thus reducing the wind pressure on them.
 Pin
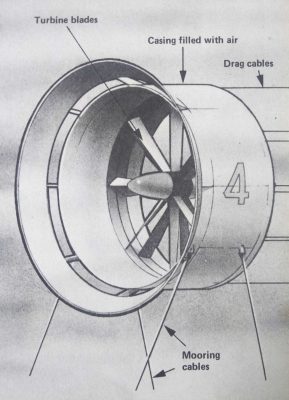
Pin OCEAN CURRENT GENERATOR
With turbine blades up to 20 metres long, turning at no more than one revolution per minute, machines like this could generate considerable amounts of electricity from great ocean currents like the Gulf Stream. They would be moored deep under water, well below the biggest ships and the effects of bad weather.
 Pin
Pin There are several energy alternatives that are currently available and considered to be "unlatched" or viable options for us. These include:
1. Solar Energy: Solar power harnesses sunlight and converts it into electricity through the use of solar panels. It is a clean and renewable energy source that can be used for residential, commercial, and industrial purposes.
2. Wind Energy: Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of the wind into electrical energy. It is another clean and renewable source that can be used on a large scale, particularly in areas with consistent wind patterns.
3. Geothermal Energy: Geothermal power utilizes the heat from the Earth’s subsurface to generate electricity or produce heat. It is a reliable and sustainable energy source that is available in certain regions.
4. Hydropower: Hydropower generates electricity by harnessing the energy from flowing or falling water. It is one of the oldest forms of renewable energy and can be obtained from rivers, dams, or tidal movements.
5. Biomass Energy: Biomass refers to organic matter such as agricultural residues, wood, or dedicated energy crops that can be converted into biofuels or burned directly to produce heat or electricity.
6. Nuclear Energy: While controversial due to safety concerns and waste management, nuclear power is a viable energy alternative that generates electricity through controlled nuclear reactions. It produces significant amounts of electricity without greenhouse gas emissions.
These energy alternatives offer potential solutions to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels, decrease environmental impacts, and contribute to a more sustainable energy future. However, the choice and implementation of these alternatives depend on various factors such as geographic location, resource availability, technological advancements, and policy frameworks.
There are several challenges that need to be addressed in order to fully unlock the potential of alternative energy sources and transition to a more sustainable energy system:
Overall, unlocking the potential of alternative energy sources and transitioning to a sustainable energy system requires a multi-faceted approach that includes technological advancements, policy support, public acceptance, and international cooperation.
Advancements in technology and innovation can play a significant role in unlocking the potential of untapped energy alternatives like tidal power or geothermal energy in several ways:
Frequently Asked Questions for Energy Alternatives :
Energy alternatives refer to different sources of energy that can be used as an alternative to traditional fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas. These alternatives aim to reduce the carbon footprint and dependence on non-renewable resources.
Exploring energy alternatives is essential for several reasons. Firstly, traditional fossil fuels are finite resources that will eventually run out. Secondly, they contribute to environmental issues such as air pollution and climate change. Energy alternatives offer the opportunity to transition to cleaner and more sustainable sources of energy, reducing these negative impacts.
There are several common energy alternatives available. These include renewable sources such as solar power, wind power, biomass, geothermal energy, and hydroelectric power. Additionally, there are also emerging technologies like fuel cells, tidal power, and wave energy.
Solar panels harness the energy from sunlight and convert it into electricity. They contain photovoltaic cells, which are made up of semiconductors that absorb photons from sunlight. These absorbed photons then release electrons, generating an electric current that can be used for various purposes.
Wind turbines are used to generate wind power. These turbines have large blades that spin when the wind blows, converting the kinetic energy of the wind into mechanical energy. This mechanical energy is then converted into electricity through a generator.
Biomass can be a sustainable energy alternative if harvested and used responsibly. Biomass refers to organic materials like wood, agricultural waste, and even byproducts from various industries. When burned, these materials release carbon dioxide, but as long as new biomass is planted to replace what is being used, the process remains carbon neutral.
Geothermal energy harnesses the heat generated from within the Earth’s crust. This heat can be used directly for heating purposes or converted into electricity through geothermal power plants. Geothermal energy is considered sustainable as it relies on the natural heat generated by the Earth’s core.
Hydroelectric power is generated by harnessing the energy of flowing or falling water. Dams are built to create large reservoirs, and when the water is released, it turns turbines, thus converting the kinetic energy of water into electricity.
The cost of energy alternatives varies depending on the technology and scale of implementation. Initially, some alternatives may seem more expensive than traditional fossil fuels, but as technologies advance and economies of scale are achieved, the cost tends to decrease. Over time, energy alternatives can become more cost-effective, making them viable options.
While it may be challenging for energy alternatives to completely replace traditional fossil fuels in the short term, they can certainly play a significant role in reducing our reliance on them. A diversified energy portfolio that combines different alternatives, along with improvements in energy efficiency, can make a substantial impact in transitioning towards a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.































